What is Domain Name Registration?
In order for website names to be recognized on the internet, a system was put in place to register domain names. There is also an organization that is responsible for the registration process, name conventions, and governance of the registrars throughout the world. This organization, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), is an international, community-driven organization and is not owned or governed by any one country.
In their own words, ICANN is defined as:
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is an internationally organized, non-profit corporation that has responsibility for Internet Protocol (IP) address space allocation, protocol identifier assignment, generic (gTLD) and country code (ccTLD) Top-Level Domain Name System (DNS) management, and root server system management functions. These services were originally performed under a U.S. Government contract by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and other entities. ICANN now performs the IANA function.
As a private-public partnership, ICANN is dedicated to preserving the operational stability of the Internet; to promoting competition; to achieving broad representation of global Internet communities; and to developing policy appropriate to its mission through bottom-up, consensus-based processes.
ICANN Archives
Simply put, domain registration is the process of registering a domain name through an official domain registrar.
When you register a domain name, it is placed in the DNS and associated with an IP address. This allows for you to find the location of that domain name using your internet browser.
Registered domain names are unique to prevent having multiple websites with the same name. Registered domains are not registered indefinitely. The registration must be renewed periodically.
What is a Domain Registrar?
A domain registrar (sometimes called a domain host) is an accredited entity that takes your domain name registration and adds it to the domain name system so that it can be recognized on the internet.
Domain registrars are accredited through ICANN and must go through an accreditation process that involves financial as well as organizational requirements before they can be approved.
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is the letters and numbers that represent an internet location identified by an IP address. When you look at a URL (which includes the domain name), it can be broken into several parts:
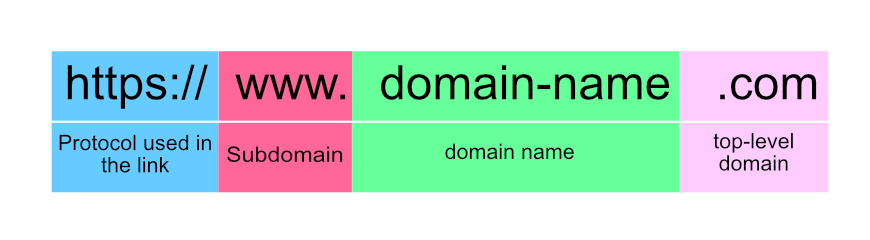
- Protocol is what is being used on the browser to connect with the website location.
- Subdomain is an additional part of your domain name. “WWW” is generally created automatically for you and was originally used to identify that it was on the “World Wide Web”.
- An example of a subdomain is other.domain-name.com. “Other” is the name of the subdomain that resides within your main domain.
- Domain name is the part of the URL that identifies your site with letters or numbers. A root domain is a combination of the domain name and the top-level domain. A domain name represents the IP address with a name that makes it easily identifiable.
- Top-level domain (TLD) is the final part of the domain name and used to identify the location based on geography or function. The original seven generic TLDs included .com, .net, .org, .int, .edu, .gov, and .mil.





